What is HTML ?
To start building beautiful websites on the web, the first thing you need to learn about is HTML.
HTML is a markup language that defines the structure of your content. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or wrap, different parts of the content to make it appear a certain way, or act a certain way. The enclosing tags can make a word or image - hyperlink to somewhere else, can italicize words, can make the font bigger or smaller, create tables and so on.
A markup language is a text-encoding system which specifies the structure and formatting of a document and potentially the relationship between its parts. Markup can control the display of a document or enrich its content to facilitate automated processing, which makes it readable to both human beings and computers.
XML, HTML are few of the examples of Markup languages which are commonly used.
Example of XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><bookstore> <book> <title>Learning XML</title> <author>John Doe</author> <year>2020</year> <price>29.99</price> </book> <book> <title>Advanced XML</title> <author>Jane Smith</author> <year>2022</year> <price>39.99</price> </book></bookstore><bookstore> The root element that contains all other elements.<book>: A repeating element, each representing a book.<title>, <author>, <year>, <price> Child elements with data about each book.As you can see, it’s pretty self-explanatory, each element represents. XML files are often used for storing data, configuration files, and data exchange.
When it comes to HTML, it has pre-defined presentation semantics, meaning that their specifications prescribe some aspects of how to present the structured data on particular media.
In the following example, whatever is written inside the tag will be displayed in bold. That’s what is meant by presentation semantics; each defined tag in HTML has a meaning, tag <b/> means bold.
<b>Bold text</b>Basic Structure
Section titled “Basic Structure”HTML is a markup language that defines the structure of your content. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or wrap, different parts of the content to make it appear a certain way, or act a certain way.
An element is predefined HTML specification which comes with a predefined semantics. In HTML, an element may contain a data item or a chunk of text or an image, or perhaps nothing. A typical element includes an opening tag with some attributes, enclosed text content, and a closing tag (if the element has a closing tag).
Lets look at a HTML element called <p> which is used to signify a paragraph.
Lets look at following text
Hello world!
If we wanted the line to stand by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in paragraph tags:
<p>Hello world!</p>Anatomy of an HTML element
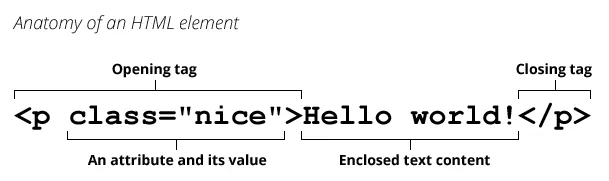
As you can see from the image, above snippet following
- opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets. This states where the element begins or starts to take effect in this case where the paragraph begins.
- closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends in this case where the paragraph ends. Failing to add a closing tag is one of the standard beginner errors and can lead to strange results.
- content: This is the content of the element, which in this case, is just text.
- The element: The opening tag, the closing tag, and the content together comprise the element.
Attributes
Attributes contain extra information about the element that you don’t want to appear in the actual content. Here, class is the attribute name and nice is the attribute value.
- A space between it and the element name (or the previous attribute, if the element already has one or more attributes).
- The attribute name is followed by an equal sign.
- The attribute value is wrapped by opening and closing quotation marks.
Type of HTML elements
Section titled “Type of HTML elements”Nesting elements
Section titled “Nesting elements”You can put elements inside other elements too, this is called nesting.
Let’s look at the text -> My cat is very grumpy,
If we wanted to state that our cat is very grumpy, we could wrap the word “very” in a <strong> element, which means that the word is to be strongly emphasized.
<p>My cat is <strong>very</strong> grumpy</p>The Browser will render this as below.
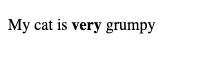
Void elements
Section titled “Void elements”Some elements have no content and are called void elements.
For example <img> element, if we want to render an image on to the page, we can use img attribute and specify path to the image asset in src attribute as value.
There is no content for this element, img element is self-closing.
<img src="../assets/happy_smiling_cat.jpg" alt="Happy catto" />Here web page will render this bad boy.
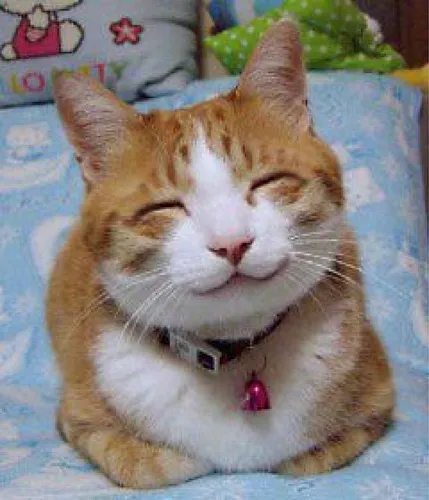

We will talk about setting up a development environment in the next section.