Semantic Elements
You may be thinking why are we starting with semantic elements rather than elements. We have already discussed HTML elements have presentational meaning, now again semantics ?? Yes. Semantic HTML elements help you define sections of a webpage to help browsers, search engines, and developers better understand the content of that webpage. This way its easier to understand what a block of html means easily just by looking at the parent element of a block.
Semantic Elements
Section titled “Semantic Elements”Semantic HTML introduces elements that provide meaning and context to the content within the HTML document. These elements help improve accessibility, SEO, and maintainability of the code by clearly describing their intended purpose.
Instead of going on and on about semantic element, lets talk about structuring content inside HTML file.
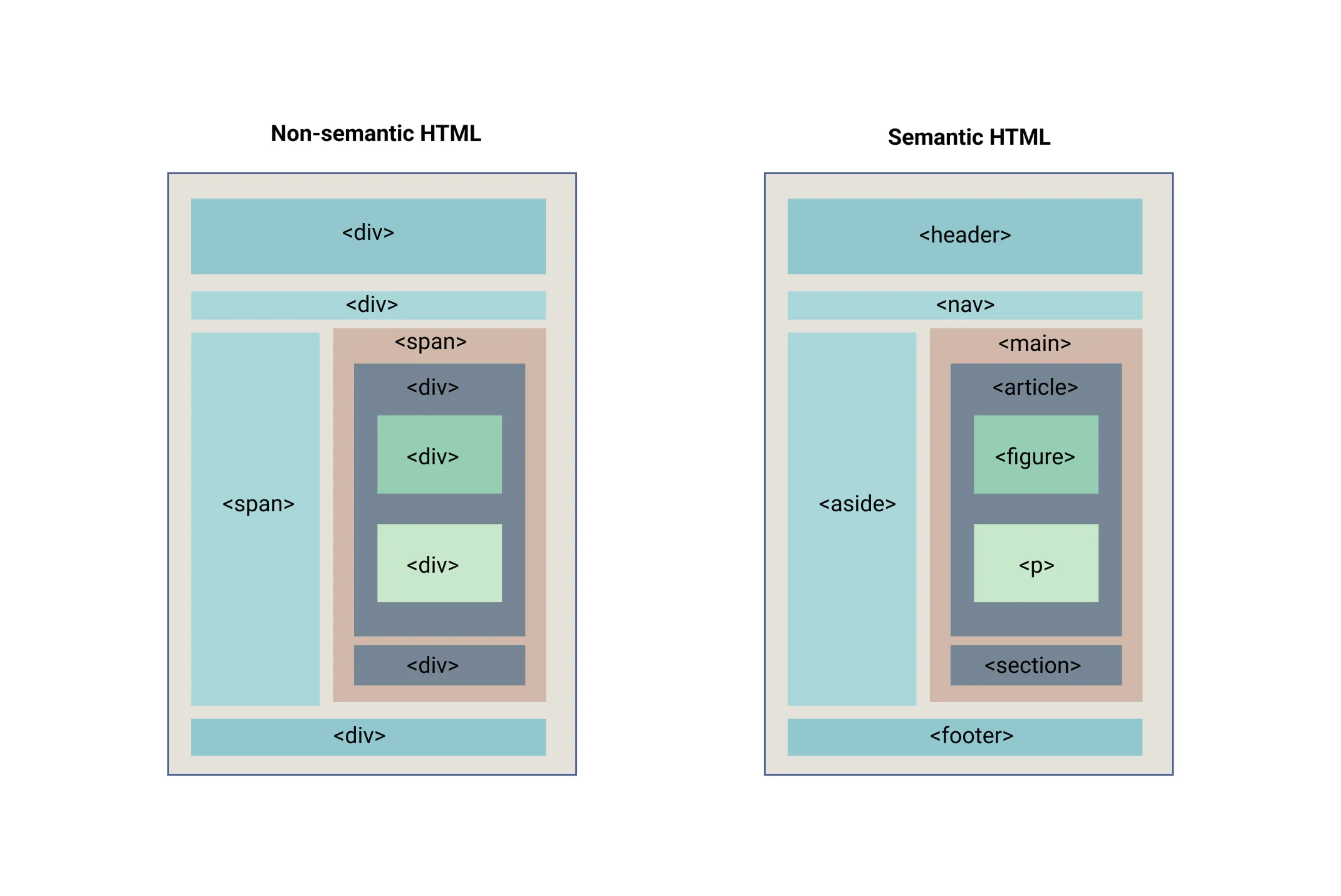
You may have seen many websites before stumbling on to this article, and you have seen sections of the website that are different from each other. This is mostly done by considering a section of the website as different blocks and adding styles to it.
For this sectioning or containerization purpose <div> or <span> element(to a limited extent) is used.
<div> Element
Section titled “<div> Element”The <div> HTML element is the generic container for flow content.
It has no effect on the content or layout until styled in some way using CSS.
It is a pure container element with no other meaning attached to it.
(From Mozilla docs)
Why & Importance of Semantic HTML
Section titled “Why & Importance of Semantic HTML”From a developer experience point of view, imagine yourself open up an HTML document and seeing all the content is separated using a just div element, and the effort you have to put in to understanding the structure just make very basic edits to the file. Here were Semantic HTML helps you, it helps in maintainability.
Thing about the web is, People who consume the website may be from different countries, cultures, sometimes it’s not even people -> bots.
It is important we keep the above in mind while building websites. Semantic html helps your website accessible to consume information for people who use assistive technologies like screen readers, making it easier to navigate and understand. You can combine semantic elements with ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and attributes to enhance accessibility further.
This applies to bots too, search engines crawling your website understands semantic html and it helps in ranking your website better.
This doesn’t mean you shouldn’t use <div> or <span> elements in the document,
but try to avoid using them if a semantic alternative is available.
Now lets go through semantic elements in HTML5
New HTML5 Semantic Elements
Section titled “New HTML5 Semantic Elements”Below are the semantic elements to help define the structure of a webpage more clearly.
-
<header> -
<footer> -
<section> -
<article> -
<aside> -
<nav> -
<header>: Represents the introductory content or a set of navigational links. Typically contains the site’s logo, title, and navigation links.<header><h1>Website Title</h1><nav><ul><li><a href="#home">Home</a></li><li><a href="#about">About</a></li><li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li></ul></nav></header> -
<nav>: Represents a section of the document intended for navigation. Typically, contains a list of links to other sections or pages.<nav><ul><li><a href="#home">Home</a></li><li><a href="#services">Services</a></li><li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li></ul></nav> -
<footer>: Represents the footer of a document or a section. Typically, contains information about the author, copyright information, and links to related documents.<footer><p>© 2025 Presevelog. All rights reserved.</p><nav><ul><li><a href="#privacy">Privacy Policy</a></li><li><a href="#terms">Terms of Service</a></li></ul></nav></footer> -
<section>: Represents a standalone section of content, typically with a heading. Used to group related content together.<section><h2>About Us</h2><p>We are a company dedicated to providing the best services...</p></section> -
<article>: Represents a self-contained piece of content that can be independently distributed or reused. Suitable for blog posts, news articles, or any other independent content.<article><h2>Article Title</h2><p>This is the content of the article...</p></article> -
<aside>: Represents content tangentially related to the main content. Often used for sidebars, navigation bars on the side, or advertisements.<aside><h2>Related Articles</h2><ul><li><a href="#article1">Article 1</a></li><li><a href="#article2">Article 2</a></li></ul></aside>
Using Semantic Elements to Structure Your HTML
Section titled “Using Semantic Elements to Structure Your HTML”Practical Examples and Best Practices:
A well-structured HTML document using semantic elements might look like this, Here you can see nesting semantic elements correctly to maintain a logical and hierarchical structure,
For example, the <header> and <footer> elements should be direct children of the <body> or relevant sectioning elements.
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Semantic HTML Example</title> </head> <body> <header> <h1>My Website</h1> <nav> <ul> <li><a href="#home">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#about">About</a></li> <li><a href="#services">Services</a></li> <li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav> </header>
<main> <section id="home"> <h2>Welcome to My Website</h2> <p>This is the home page of my awesome website...</p> </section>
<section id="about"> <h2>About Us</h2> <p>We are a company dedicated to providing the best services...</p> </section>
<section id="services"> <h2>Our Services</h2> <article> <h3>Service 1</h3> <p>Description of Service 1...</p> </article> <article> <h3>Service 2</h3> <p>Description of Service 2...</p> </article> </section>
<aside> <h2>Related Articles</h2> <ul> <li><a href="#article1">Article 1</a></li> <li><a href="#article2">Article 2</a></li> </ul> </aside> </main>
<footer> <p>© 2024 My Website. All rights reserved.</p> <nav> <ul> <li><a href="#privacy">Privacy Policy</a></li> <li><a href="#terms">Terms of Service</a></li> </ul> </nav> </footer> </body></html>